Blockchain, which was first developed to support Bitcoin, has experienced an amazing development. Its original intent has been exceeded, and it now has the potential to completely transform a number of industries. A thorough examination of the numerous applications of blockchain technology is what this article wants to do.
What is Cryptocurrency ?

Blockchain technology’s history is heavily influenced by cryptocurrencies, which are frequently the first use cases that come to mind when considering the technology. It represents a digital or virtual form of money that uses the security and decentralization of the blockchain to enable safe and open transactions. Blockchain entered the public consciousness thanks to Bitcoin, the original cryptocurrency.
The Key Components of Blockchain
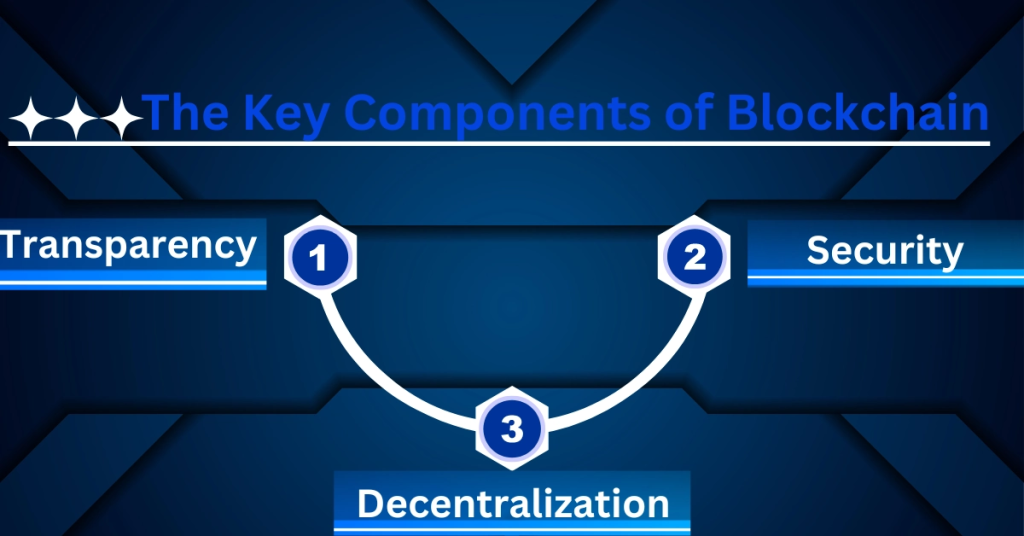
Decentralization:
Instead of utilizing a centralized authority, blockchain relies on a network of computers, or “nodes.” There is no single point of failure due to this decentralization, which ensures confidence and durability.
Transparency:
All users of the network can see the transactions’ records on a public ledger. Transparency increases accountability and trust, which lowers the risk of fraud.
Security :
Blockchain uses cryptographic methods to protect data. When information is captured, it is almost impossible to change or tamper with it, protecting the accuracy of the data.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Blockchain technology’s history is heavily influenced by cryptocurrencies, which are frequently the first use cases that come to mind when considering the technology. It represents a digital or virtual form of money that uses the security and decentralization of the blockchain to enable safe and open transactions. Blockchain entered the public consciousness thanks to Bitcoin, the original cryptocurrency.
Blockchain Technology Timeline
To appreciate the current state and future potential of blockchain, it’s essential to examine its evolution over time.
Early Beginnings (2008-2009)
The adventure starts with the invention of Bitcoin by the eponymous Satoshi Nakamoto. Blockchain technology and the idea of digital currencies were both established by the Bitcoin whitepaper.
Expanding Horizons (2010-2015)
As alternative cryptocurrencies like Litecoin and Ripple were available, the market became more diverse. The blockchain was first used by Ethereum, a critical milestone that made it possible for agreements to be self-executing.
Maturing Technology (2016-2020)
Major businesses and organizations started investigating blockchain for a variety of application cases. They saw how it could increase transparency and efficiency. Industry-specific consortiums were established to promote interaction and innovation.
The Present and Beyond (2021-Present)
The market for art and antiques has undergone a revolution since Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) first appeared in recent years. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms have become very popular, changing the way that traditional financial services are provided.
Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrency
The applications of blockchain technology in various industries demonstrate the technology’s adaptability. In this section, we’ll examine ten notable application cases that eloquently demonstrate its transformational ability.
What is Blockchain?
It’s important to understand the underlying principle of blockchain before we look at its many applications. Blockchain is fundamentally a decentralized, distributed ledger that safely and permanently records transactions across numerous computers. The blocks in the chain are connected by cryptographic hashes and each block in the chain comprises a series of transactions.
1. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain improves supply chain transparency and traceability, lowering fraud and guaranteeing product authenticity. This is especially useful for sectors like the food industry where customers want to know where their food is coming from and how safe it is.
2. Healthcare
Blockchain encourages efficiency and data security by safely storing and sharing patient records amongst healthcare providers. Patients have more control over their data, while healthcare practitioners gain easier access to vital data.
3. Voting Systems
Voting systems that are based on blockchain are safe, open, and unhackable. The technology can greatly lower the danger of electoral fraud and guarantee the fairness of elections by recording votes on an immutable ledger.
4. Intellectual Property
Through the creation of unchangeable ownership and usage records, blockchain protects intellectual property rights. Secure and open protection against piracy and unlawful use of a creator’s work benefits artists, writers, and other creators.
5. Real Estate
Blockchain streamlines real estate transactions by storing ownership information and transaction history on an unchangeable ledger. This lessens the need for middlemen, simplifies the purchasing and selling process, and increases transparency.
6. Cross-Border Payments
Both individuals and businesses involved in international transactions benefit from blockchain’s reduction of fees and transaction times in cross-border payments. It provides a more effective and affordable substitute for conventional banking systems.
7. Identity Verification
Blockchain improves identity verification procedures by allowing for transparent and secure ownership over personal data. While lowering their risk of identity theft and fraud, individuals can keep control over their digital identities.
8. Gaming
The gaming business has been transformed by the introduction of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) on the blockchain. Digital collectibles and in-game items are now really owned by gamers, opening up new revenue opportunities and encouraging a sense of ownership.
9. Energy Trading
Blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading, enabling people and companies to effectively swap surplus energy. This encourages the utilization of renewable energy sources, therefore promoting sustainability.
10. Charity and Aid
Blockchain guarantees accountability and traceability for donations to charities. Donors and recipients may both track how their gifts are used, which promotes confidence. The likelihood of money being stolen is lower because of this transparency.
Conclusion
It has been a revolutionary and hopeful journey for blockchain technology from its cryptocurrency roots to its present position. The technical environment is still being shaped by its fundamental characteristics of decentralization, security, and transparency. Looking ahead, blockchain technology’s potential is limitless and promises to continue causing upheaval in a variety of industries.
FAQs
1. What is the primary advantage of blockchain technology?
Blockchain’s main advantages are its decentralization and tamper-resistance, which improve security and transparency in a variety of applications. As a result, there is no longer a need for middlemen, and participant trust is increased.
2. Can blockchain be used for small businesses?
Yes, blockchain technology may help small firms by lowering operational costs, enhancing security, and opening up new revenue sources through cutting-edge applications like supply chain management and safe data exchange.
3. Is blockchain environmentally friendly?
The environmental impact of blockchain varies depending on the particular blockchain network and its consensus algorithm. While certain blockchains, like Bitcoin, use a lot of energy, other blockchains are made to be more environmentally friendly. New technologies are attempting to address these environmental issues.
4. How does blockchain impact data privacy?
Blockchain improves data privacy by enabling transparent and safe control over personal data. Users now have more control over their data, and blockchain records’ immutability lowers the possibility of data breaches and unwanted access.
5. What challenges does blockchain technology face?
Blockchain must be widely adopted and overcome obstacles like scalability and regulatory compliance. These problems are being addressed and the technology’s full potential is being unlocked through ongoing research and development.





