Introduction
Cloud computing has developed into a crucial technology that underpins several internet services and applications in today’s quick-paced digital world. Cloud computing probably comes into play whenever you stream films, access your email, or work together on a project. Cloud computing, though, is what exactly? What are the advantages of it, and how does it function? We shall delve into the numerous facets of cloud computing in this essay as we explore its intriguing world. A few of the top cloud computing companies include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
Cloud computing is revolutionizing AI by providing scalable resources for data storage and processing, enabling advanced AI applications. The future of Artificial intelligence lies in its seamless integration with cloud services, fostering innovation and accessibility.
What is Cloud Computing?
2.1 Understanding the Cloud Computing Definition
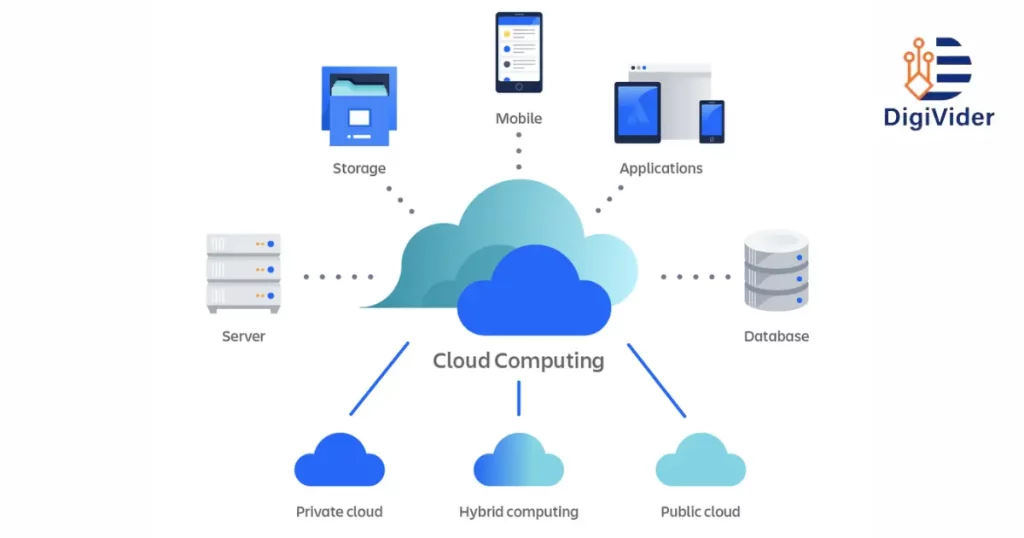
Cloud computing describes the provision of computing services via the Internet. Through the use of remote servers, users of cloud computing can access and store data, programs, and resources without relying on a local server or a personal computer. Users can more easily access information from any location with an internet connection because these servers are hosted and operated by outside companies. This is the answer to what is cloud computing.
2.2 How Cloud Computing Works
An extensive network of distant servers linked by the internet underlies cloud computing. Redundancy and dependability are ensured by the distribution of these servers across various data centers. The cloud system responds to a user’s request for data or services by obtaining the necessary data from these servers and sending it to the user’s device.
2.3 Cloud Computing as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the three primary types of services offered by cloud computing. The amount of control and flexibility each of these services gives users varies.
2.4 The Benefits of Cloud Computing
The technology used by both people and companies has been changed by cloud computing. Cost reductions, scalability, flexibility, automatic upgrades, and improved cooperation are some of the major advantages. A suite of potent applications and services is also accessible to organizations and consumers through Google’s cloud computing.
Who is Using Cloud Computing?
3.1 Cloud Computing in Businesses
Cloud computing has taken over as the main operating system for many businesses. Large amounts of data can be safely managed and stored by businesses, which can also grow their infrastructure to meet changing demands and collaborate effectively across teams.
3.2 Cloud Computing in Education
Additionally, the education industry is adopting cloud computing. By enabling access to online resources, e-learning platforms, and remote learning opportunities, educational institutions may reach a wider audience.
3.3 Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Within the healthcare sector, cloud computing is essential. It enhances patient care and outcomes by enabling healthcare providers to safely retain patient data, support telemedicine, and get immediate access to vital information.
3.4 Cloud Computing in Government
For operational efficiency, improved data security, and effective public services, governments all around the world have embraced cloud computing.
The Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing with Google offers scalable and flexible solutions, including virtual machines, storage, databases, and AI services, empowering businesses to innovate, collaborate, and grow efficiently in the digital era. Innovative job in cloud computing. Manage data, apps, and services for seamless business operations.
4.1 Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are two of the biggest benefits of cloud computing. Without the bother of managing physical infrastructure, businesses can rapidly scale their resources up or down based on their needs.
4.2 Cost Savings
Businesses and individuals can save money by using the cloud to replace expensive on-premises technology and reduce maintenance requirements.
4.3 Increased Collaboration and Accessibility
As data and programs can be accessible from any location with an internet connection thanks to cloud computing, team collaboration among members is made simple.
4.4 Automatic Updates and Maintenance
To guarantee that users always have access to the newest features and security fixes, cloud service providers take care of routine upgrades and maintenance. Salary cloud computing varies based on roles and experience. In-demand cloud skills like AWS, Azure, and GCP can command competitive pay in the tech industry.
Types of Cloud Computing
5.1 Public Cloud
Public clouds are available to the general public since they are owned and run by outside service providers. Both small and medium-sized organizations and individuals can use these cloud services because they are affordable.
5.2 Private Cloud
A single organization might have more control and customization possibilities with private clouds because they are dedicated to that entity. For companies with particular security and compliance needs, they are perfect.
5.3 Hybrid Cloud
Organizations can store sensitive data on a private cloud while utilizing the scalability of the public cloud thanks to hybrid clouds, which integrate the benefits of both private and public clouds.
Pros and Cons of Different Types of Services
Cloud computing as a service has many advantages that are given below:
6.1 Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Virtual machines, storage, and networking are all provided by IaaS as virtualized computing resources via the Internet. Although there is a lot of freedom, more technical knowledge is needed.
6.2 Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Without worrying about the supporting infrastructure, PaaS enables developers to create, distribute, and maintain apps. Though the customization options may be constrained, they streamline the development process.
6.3 Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS does not require installation or maintenance and instead delivers fully functional software programs over the Internet. Although it is user-friendly, customization options may not be as broad.
Is Cloud Computing Safe?
7.1 Data Security in Cloud Computing
Regarding cloud computing, data security is of the utmost importance. To guard user data from unauthorized access, cloud service providers put strict security procedures in place.
7.2 Privacy Concerns
Cloud service providers place a high priority on data privacy, but users must also take the proper security measures to protect sensitive data.
7.3 Backup and Disaster Recovery
When calamity strikes, data is still safe and accessible because of the dependable backup and disaster recovery options provided by cloud computing.
Conclusion
The way we save, use, and access information has been completely transformed by cloud computing. Its scalability, affordability, and collaborative features have elevated it to the status of a technology that is essential to both individuals and corporations. Cloud computing will become even more crucial in determining how we live in the future as we continue to embrace the digital age.
FAQs
Q: What is cloud computing?
A: Cloud computing is the transmission of computing services over the internet, enabling users to access and store data, applications, and resources remotely.
Q: What are the benefits of cloud computing?
A: Cloud computing provides cost savings, scalability, flexibility, automatic upgrades, and improved cooperation.
Q: Who uses cloud computing?
A: Everybody uses cloud computing, including people, companies, organizations that offer healthcare, education, and the government.
Q: What are the different types of cloud computing services?
A: The three primary categories of cloud computing services are software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
Q: Is cloud computing safe?
A: Cloud service providers put robust security mechanisms in place to secure customer data, making cloud computing typically safe. To protect the confidentiality of their data, users must also adopt the required security measures.







